 Cardiac Drugs for NCLEX part 1
Cardiac Drugs for NCLEX part 1
Mechanisms Regulating Arterial Pressure
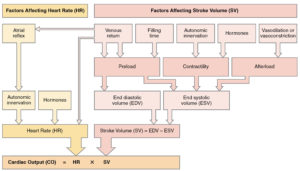
- ANS helps control pressure by adjusting cardiac output (HR x SV) and peripheral resistance.
- The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system helps control arterial pressure by:
- -Releasing angiotensin II – potent vasoconstrictor of arterioles and veins
- -Releasing aldosterone – promotes Na+ and H2O retention by kidneys
- Vasopressin (ADH) is a potent vasoconstrictor and increases water reabsorption.
- Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is a vasodilator and causes increases excretion of Na+ and H2O by kidneys. It also inhibits renin
- Decreasing blood volume and dilating arterioles and veins help control BP
Epinephrine
Expected Action:
- Binds to: α1 – > vasoconstriction
β1 – > increased HR, contractility, & AV conduction
β2 – > Bronchodilation
Epinephrine (Adrenaline) – Catecholamine Adrenergic Agonist
Therapeutic Uses:
decreased absorption of local anesthetics or extravasated meds
Manage superficial bleeding
decreased congestion of nasal mucosa
increased BP
Treatment of AV block and cardiac arrest
Asthma
Adverse Effects:
Hypertensive crisis
Necrosis from extravasation
Dysrhythmias / increased myocardial O2 demand – > angina
Contraindications/Precautions: Pregnancy (C)
Interactions:
MAOIs – > increased effect and duration
TCAs block uptake of epi.
General anesthetics – > lead heart to be hypersensitive to epi – > dysrhythmias
α-adrenergic blockers (phentolamine
β-adrenergic blockers (propanolol)
Education:
Stop infusion with evidence of extravasation; treat with α-blocker (phentolamine)
Dopamine
Dopamine (Intropin) – Catecholamine Adrenergic Agonist
Expected Action:
Low Dose (Dopamine receptors) – > Renal vasodilation
Mod Dose (Dopamine, β1) – > Above + increased HR, increased contractility, increased AV conduction
High Dose (Dopamine, β1, α1) – > Above + vasoconstriction
Therapeutic Uses:
Shock, Heart failure
Contraindications/Precautions:
CI: Pheochromocytoma, Pregnancy (C)
Adrenergic Receptors
α1 — Vasoconstriction of arterioles in skin, viscera, and mucous membranes, and veins
β1 — increased HR, increased contractility, increased AV conduction, Release of renin in kidneys
β2 — Vasodilation of arterioles in heart, lungs, and skeletal muscle, Bronchodilation, Relaxation of uterine smooth muscle, Glycogenolysis in liver, Skeletal muscle contraction
Dopamine — Vasodilation of renal blood vessels
Dobutamine
Dobutamine (Dobutrex) – Catecholamine
Expected Action:
- Binds to: α1 – > vasoconstriction / β1 – > increased HR, contractility, & AV conduction
β2 – > Bronchodilation
Therapeutic Uses:
Heart failure
Adverse Effects:
ñ heart rate
Contraindications/Precautions:
Pregnancy (B)
Education:
Stop infusion ĉ evidence of extravasation; treat with α-blocker (phentolamine)
α-Adrenergic Blockers
Examples : Prazosin (Minipress) – Others: doxazosin mesylate (Cardura), Phentolamine (Regitine), ergotamine tartrate
Expected Action:
Selective α1 blockade resulting in venous and arterial dilation
Therapeutic Uses:
Hypertension
Phentolamine: Extravasation of adrenergic agonists
Doxazosin mesylate: ò symptoms of benign prostatic hypertrophy
Adverse Effects:
First-dose orthostatic hypotension (monitor BP for 2 hrs post-treatment)
Contraindications/Precautions:
Pregnancy (C)
Interactions:
Antihypertensives – > additive hypotensive effect
NSAIDs / clonidine – > decreased antihypertensive effects of prazosin
